Understanding Pulsed-Light Photonic Curing
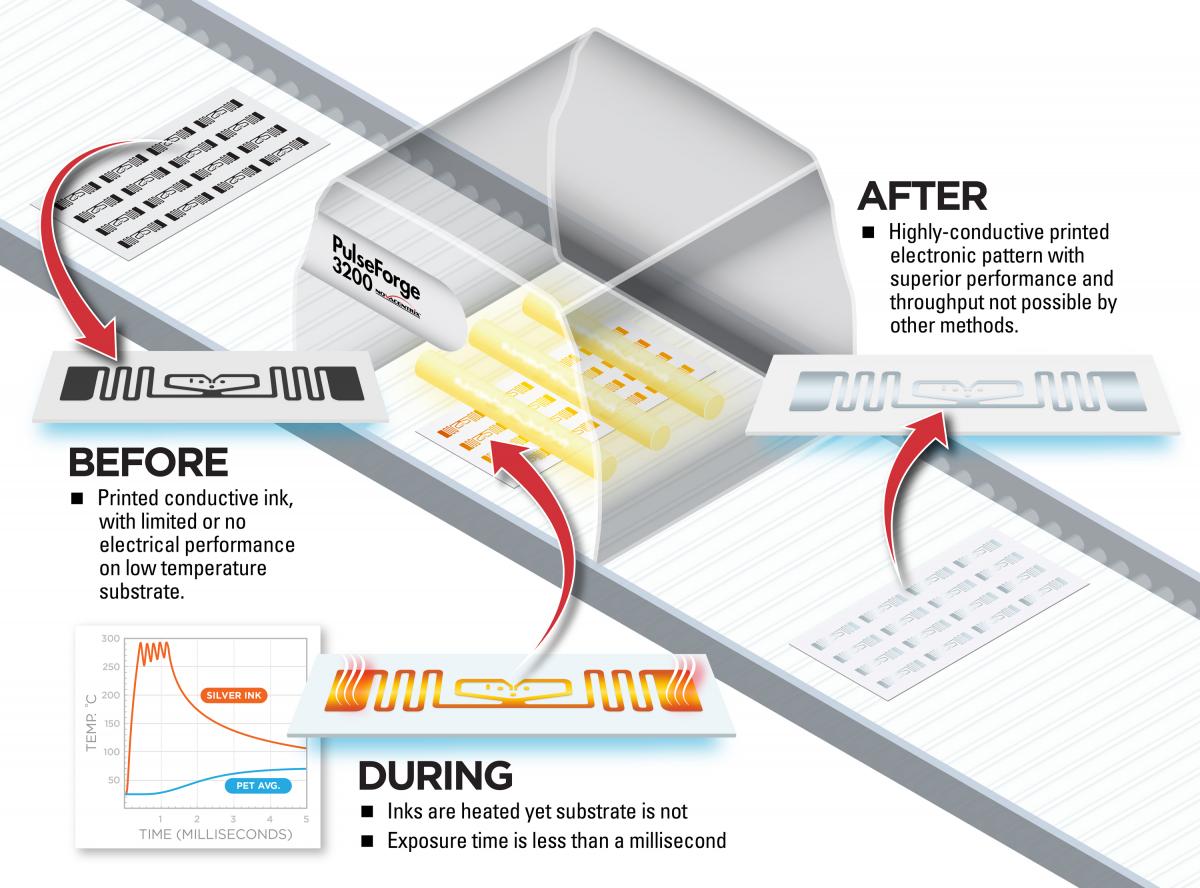
What is pulsed-light photonic curing?
Why Does This Matter?
- As compared to traditional thermal processing equipment, e.g. ovens, photonic curing tools have a tiny footprint.
- Equipment can be retrofitted onto existing lines or simply take up less space in a clean room for the same processing rate.
- Since higher processing temperatures can be achieved, improved conductive performance can be achieved with functional materials.
- Inexpensive or thinner substrates can be substituted for more traditional ones.

What are the Applications of Pulsed-Light Photonic Curing?
The maturing complexity of modern printed electronics for customer applications demands high throughput manufacturing and improved device function. The functionality of the printed electronics is critically important as customers demand more out of each device. In that order, multiple layers are designed into each device, requiring ever more versatile processing techniques.
Modern Design
Photonic curing is uniquely suited to complement the processing needs in the manufacture of modern printed electronics. The photonic curing process can provide a fast, reliable and transformative processing step to meet the most demanding production designs.
Reduced Heat
Photonic curing enables lower thermal processing budget with current materials, and it can provide a path to incorporate more advanced materials and functionality into future printed electronics.
Process Flexability
In addition to sintering metals and ceramics, photonic curing is also used to dry thin films, modulate chemical reactions, and even anneal ceramics and semiconductors such as Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) and amorphous silicon.